Becoming older, staying younger and being happier

When was your last hospital visit? Do you remember the piles of paper you were facing, the forms you were filing, and the systems the doctors were using to write down your diagnosis?
With doctors being on average 51 years old, innovation finds slow adoption in the healthcare industry [1].
Challenges are rising for privacy and regulations, too. Despite the intrinsic sharing nature of the internet, human-specific information and data becomes more difficult to access. This creates localized expertise while prohibiting shared and centralized facilitation of the best possible treatments.
Nevertheless, with the current catalysts in robotics, machine learning and biotech, innovative forces push the healthcare sector closer to adoption. Stacking the odds against stagnation and towards inevitable adaptation.
The Landscape of Opportunity
Robotic companions for children, personalized medication, early-stage diagnosis, healing strokes, high precision operations and 10x faster drug development. Many exciting developments can be observed in healthcare.
Ready to take a closer look?

#1 – Operation & Robotics
One of the emerging technologies is the use of high precision robotic tools which are operated by doctors.

Due to the significant doctor enhancement in terms of precision and available information on-screen, patients benefit from reduced pain, less blood flow, lower risk of infection and ultimately shorter hospital stays leading to a faster return to normal activities.
While the robotics integrate necessary intelligent functionality for routined procedures they are less about self-performance and more about providing the necessary tools for highest precision and flexibility for doctors.
So far operation types such as cardiac, cholesterol, gynecology, general, head and neck as well as chest are covered. [2]
#2 — Care & Robotics
With constantly growing numbers of elderly, the care and nursery field is struggling with a big gap between demand in human resources and its supply. Besides elderly care, this statement stands true for child care in hospitals, too.
Reshaping elderly and childcare with affordable and scalable solutions is therefore a primary target.
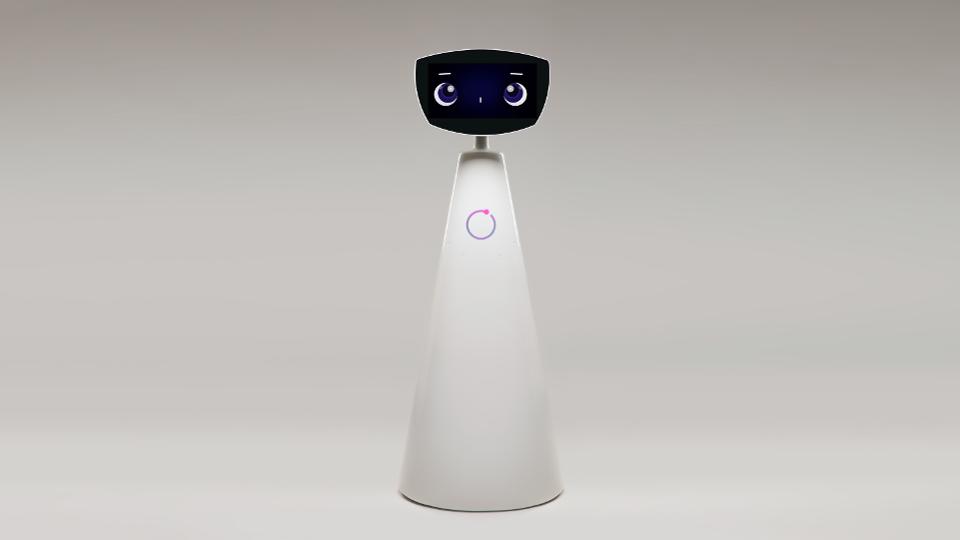

Robotic companions, like Robin from Expper Tech as shown above, are currently enrolled in the biggest hospitals from Los Angeles, California.
Medical experts from the LA hospital report that Robin has very child-friendly design, appeals to children and AI-based emotional intelligence helps Robin to build human-like conversations.
Children, which commonly face traumatic experience during hospital stays are entertained with Robin doing jokes or playing interactful games. In addition, Robin informs about the upcoming medical procedures which therefore seem less scary and reduces the time for preparing children by up to 40%, the CEO, Karén Khachikyan shared in an interview we conducted.
#3 — Patient Diagnosis and Treatment
One of the very hot topics in healthcare innovation is early and personalized diagnosis.
Imagine you visit your doctor for your routine checkup. Even though you feel perfectly healthy, the doctor may identify that Type-2 Diabetes may further develop to an inflection point. Hence, proper treatment can be prescribed early on.
Nevertheless, treatment prescription is eventually risk management, with one risk of predicting a potential future disease wrongful at the expense of finance or health.
If however the disease is identified correctly, the second emerging trend is personalized treatment. Everybody responds differently to medicine. Hence, prescribing the right product at the right doses may create major cost savings and effectivity and the perfect transition to the next chapter.
#4 — Genomics
Building on personalized treatment genomics provides the foundation in determining the best doses and medication for the patient.
Studies, such as Racial and ethnic differences in response to medicine from National Medical Association, have shown that genetic variations among different ethnicities and individuals impact the effectiveness of certain drugs and people’s responses to these drugs.
Hence, machine-learning can be used to determine the most effective medication dosage, reducing healthcare costs for the patients and providers.
In addition, disease propensity helps to understand the likelihood of a disease to occur.
#5 — Drug Development in Pharma
So far we have covered early diagnosis and personalized treatment, which may result in new developments of drugs. The big problem: From drug discovery to market takes at least 10 years [3].
With AI this process can be accelerated significantly.
The main areas where AI is currently employed by big pharma start by understanding the mechanisms of a disease which helps to generate data and models for further knowledge acquisition. In addition, existing drugs can be repurposed and new novel drug candidates generated, validated and optimized. Another area is preclinical experiments and clinical trials, where AI is being used for design, recruitment and optimization.
Assuming all steps from drug discovery to market are enhanced by machine learning, the entire process may be shortened all the way down from ten years to just one year [4, 5].
#6 — Brain Research
The final presented area is brain research where things become wild! Not only does AI benefit neuroscience but also neuroscience benefit AI.
Let’s start with AI for neuroscience!

The first exciting area is decoding the brain with AI. Non-invasive Electroencephalogram (EEG) is commonly used to measure brain behavior.
With the help of EEG, we can observe which areas of the brain are activated when trying to move the arm. Let’s assume a patient had a heart attack and after luckily waking up, he or she is unable to move the arm.
To relearn arm movement, we may now train an artificial neural network and identify to which inputs or stimulations, the areas for arm movement is most sensitive to. Similarly, these inputs can then be given to the patient to enhance the readaptation of arm movement.
To further enhance the accuracy of brain activation, invasive techniques become necessary which help in tracing back source signals to identify core features and how they translate to mental states. One trending company that employs invasive techniques is Neuralink [6].
Common use cases are early diagnosis of brain diseases such as Alzheimer’s or analysis of recovery on traumata or related fields.
For applying brain research towards AI, the learning behavior of humans are studied to infer how artificial neural networks may be trained in the future. Besides reinforcement learning, where a task is repeated with a reward function to incentivize learning in the right direction, other techniques evolve, which help the AI to generalize and learn more similar as humans do.
For further questions feel free to reach out by mail or discover further related articles to AI Opportunities and Safety.
Further reading: AI in Travel – Why it’s time to pay attention!
Acknowledgments
Karén Khachikyan — CEO of Expper.Tech — Expper.Tech and Robin, LinkedIn
Egor Revkov — PhD in Genomics & Computer Science at NUS, Singapore — LinkedIn
Tushar Chouhan — PhD in Computer- & Neuroscience at NTU, Singapore — ResearchGate
References
[1] — Physicians getting older[2] —DaVinci Surgery
[3] — Drug Development Duration
[4] — Medical Drug Enhancement Areas
[5] — Drug Discovery Process
[6] — Neuralink
Image Credits
Featured Image: Photo by Laura Ring Photography on Pinterest
In-post Photo: Pictures created by author, July 2020, as well as Unsplash.com or linked below image