By 2020, 50% of analytical queries will be generated via search, NLP or voice, or will be automatically generated. – Gartner
2019 may well be the inflection point for conversational artificial intelligence (AI) adoption, going by the recent advances this technology has made on the ground. For years, there’s been din in the market; that AI is arriving. In 2018, it only got shriller – with an upsurge in published papers, events, media glare, investments and more, and actual real-world implementations, bringing the possibilities of conversational AI closer to the world. While it’s thrilling to see a new idea hit the ground and set about the changes it promises to bring, the next 18 months will be crucial for the success of conversational AI.
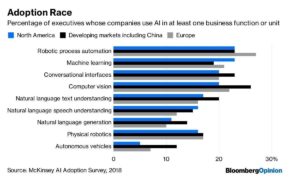
For now, the prospects seem optimistic. A recent McKinsey survey that tracked the percentage of executives whose companies are using variants of AI in at least one business function or unit, has found an increased thrust on applications such as image detection, voice enablement, natural language understanding, voice search, translation, and data mining.
What’s unique about Conversational AI
When combined and used in specific contexts, these technologies – NLU, NLP, NLG, and machine learning – are helping build powerful conversational systems with marked features such as:
- Conversational intelligence that goes beyond natural language understanding. Today, you have the ability to glean understanding from conversations – whether in spoken or written form – by analyzing content at an organizational level, using domain-specific models. This way, you derive insights from huge piles of data captured in conversations.
- Platforms with simplified bot development processes. A plethora of platforms are now available in the market that facilitate the design, development, management, and operation of conversational solutions leveraging natural language enabling technologies and third-party APIs.
- Proliferation of human-machine interactions in natural language. Chatbots have come of age with enhanced abilities to simulate intelligent conversations with humans in natural language. Most times, these interfaces that are non-industry specific, and apply across a range of domains and functions.
- Regular messaging turning intelligent. Our ubiquitous messaging platforms such as email, text messages, and other human-to-human communication – can now be programmed to be smarter with a range of possibilities to ease communication.
- Voice assistants with a range of capabilities. Spoken, conversational interfaces, that come embedded in hardware devices, and enable spoken interaction and connect with cloud-based ML capabilities.
Each of these, again, have a specific growth trajectory with deep implications for the industry.
Intelligent virtual assistants (IVAs)
Take the improvements in NLP technology, for instance, with reference to virtual customer assistants (VCAs) in customer service. Gartner predicts that by 2020, 25% of customer service and support operations will integrate virtual customer assistant technology across engagement channels, up from less than 2% in 2015.
In near future, virtual assistants will be the first line of interaction with customers in the coming decade, just like the way the 1990s were dominated by the telephone call center and the 2000s saw the shift to websites and email.
Virtual assistants will form a synergy with other digital solutions such as IoT, analytics and image recognition, and will become an interface that compiles the information from these devices to offer meaningful insights to users. Combining with advanced analytics capabilities, VCAs can also process information much faster than human agents and will predict consumer needs and behavior.
Everest Group’s latest Market Report explains the trends that are shaping its adoption: “In the last 12-14 months, the market has witnessed a gradual shift from rule-based solutions to AI-driven IVA solutions, which come with enhanced capabilities for solving much more complex interactions such as sales and marketing, payment collections, employee support, and customer acquisition and retention. IVAs can enhance the overall customer experience, and significantly change the face of front-office operations for enterprises, with increased collaboration with human agents enhancing their efficiency.”
The report commends the role of providers like Kore.ai who are driving IVA innovation and adoption by offering “an all-in-one chatbot platform (as a service) and cutting-edge smart technology for enterprises to build and deploy out-of-the-box or completely customized chatbots for their customers and workforce”.
“We were impressed by several aspects of Kore.ai’s offerings, including different intent matching models to understand customer concerns more accurately and offer more relevant results, pre-built IVAs for specific industry and function use cases, and support for reuse of components for faster IVA development. We also appreciated Kore.ai’s customized solutions and expanding capabilities in areas such as sentiment analysis, training, language, and support.”
– Sarah Burnett, Everest Group Executive Vice President and Distinguished Analyst
In essence, many first-level support requests will be handled by VCAs, freeing call center and customer engagement employees from routine tasks and enabling them to handle escalated customer issues that require more time or personal interaction. These include:
- Online travel booking providers deploy VCAs to provide tailored suggestions based on customers’ recent searches and booking history. Customers can talk to these bots at any hour and get help on a variety of issues, such as booking or changing a flight, booking a hotel room, making restaurant reservations, or getting suggestions of local tourist attractions based on user preference and seasonality.
- Restaurants use them to manage reservations, respond to customer inquiries and customize customer orders, freeing up employees to spend time with the customers.
Other virtual assistants are also rising in prominence
- Virtual support agents (VSAs) are virtual assistants that provide IT support and assistance in collaboration with the IT service desk. They pull information from knowledge management sources and an ITSM tool to provide answers to common questions. They extend chatbot capabilities by also taking action on behalf of the business user to do things like reset passwords, deploy software, escalate support requests and carry out changes to restore IT services.
- Virtual enterprise assistants (VEAs) are conversational interfaces for employees to simplify their access and engagement with the enterprise and its systems.
- Virtual personal assistants (VPAs) are generalist assistants for users that broker first-, second- or third-party services, and knowledge, commonly deployed on consumer or dedicated devices.
These examples show that with time, AI-powered virtual assistants or chatbots will evolve into tools for enterprise business transformation beyond just being conversational interfaces. We will see enterprises, which have been using virtual agents for automating and addressing customer queries, extend them to take action after customer requests. Enterprises will achieve the real value when conversational AI is used for business transformation by connecting conversations to business systems.
Voice enablement
Voice will be the most essential capability for future conversational platforms because the potential savings from automating voice communication are greater than automating text-based chat.
Today, more than 43 million Americans own a digital assistant or a smart speaker such as Amazon Alexa or Google Home (Source). There have been significant product releases from Amazon, Apple, Microsoft, Google, Samsung, Baidu, and others, with vendors flooding the market.
Consumers use these digital assistants to get news and weather updates, play music, control devices, order food or other items, listen to audiobooks and podcasts, and get flight information, to name a few.
Voice conversations tend to be more nuanced, and specific capabilities need to be built into the interfaces to understand interruptions, cues and tone-of-voice signaling, which is currently beyond the scope of most implementations.

While the focus has mostly been on consumer audience, it may shift gear in 2019 with businesses moving to leverage voice-based assistants for enterprise functions. These include workplace tasks, such as scheduling, basic information searching and assisted conference calls, as well as more complex operations including handling email, processing expense reports, and providing augmented intelligence capabilities and other deep conversational features.
Currently, voice assistants are off the mark (according to research firm Cognilytica’s benchmark study) when it comes to critical intelligence and common sense reasoning needed to assist with most critical enterprise tasks. However, vendors are gearing up to increase the intelligence in their products.
Conversational AI-powered search
More users for AI-powered assistants, and in new ways, implies that sooner than later demand for advanced conversational AI-powered search will crop up significantly.
Voice search will revolutionize the way consumers search online.
Consider, for instance, you are looking for restaurants in a new city you have just relocated to. Instead of typing in a search query like “Italian restaurants Boston,” consumers will be able to speak their search queries using a more conversational phrase, like, “How many Italian restaurants are there in Boston?”.
AI-powered search engines will do more than just providing users with a number of eat outs; they’ll also receive more conversational answers. Search engines could follow up with questions to provide more detailed solutions by asking, say:
- How many tables do you want to book?
- What location would you prefer to dine at?
- Would you prefer a pool-side table?
According to research by Alpine.ai (now acquired by Headspace), about 1 billion voice searches are being performed monthly in 2018. By 2020, 50% of all searches will be voice searches.
“Voice search has the potential to disrupt the way we market to consumers in 2019 and can play a crucial role in achieving relevant, consistent omnichannel engagement. Each touchpoint is an opportunity for marketers to enhance their customer intelligence to learn more about their customers, and with more and more channels emerging on a regular basis, these touchpoints are invaluable.”
- Christopher Hansen, Chief Product Officer, at IgnitionOne
With voice search, marketers will be able to understand the context of the conversation, analyze customer interactions, user location, preferences, demographic, and transactional data; and use it all to enhance the organization’s marketing activities.
Pre-trained bots and third-party data sets
As data powers AI, huge amounts of high-quality training data are needed to train machine learning algorithms to get predictive and yield good analytical results. We will see enterprises able to choose from a variety of free and paid algorithms and models that cover a variety of categories, including computer vision; natural language processing; speech recognition; text, data, voice, image and video analysis; and predictive analysis. 2019 will be the year that pre-trained machine learning models, third-party data sets and models, and open source training data will pick up.
Image recognition
Improved image-recognition has worked wonders in various fields. Recently, Google demonstrated an advanced imaging system for grading prostate cancer that does it more accurately than trained pathologists, and a Stanford team has achieved similar success with skin cancer.
Image recognition when clubbed with conversational interfaces expands the scope of their work manifold. With image recognition, virtual assistants can sift through information much faster than humans and are less error-prone.
Meanwhile, building facial recognition into virtual assistants helps industries such as banking, fintech, and insurance implement better security mechanisms.
Consolidation in Conversational AI market
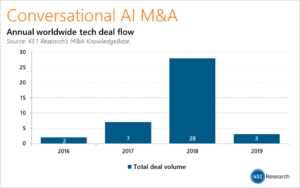
As more enterprises plan to add voice recognition and text-to-speech capabilities into both their products and customer services channels, we also witnessing a gradual consolidation in the market with a gradual rise in the number of Conversational AI deals in 2019, says a recent 451 Research study.
In 2018, the number of acquisitions driven by conversational AI or chatbot technology rose by four times. (Qlik acquired Crunch Data to enable conversational queries in its business intelligence software; Yodlee Inc bought Abe AI to enable banks to interface with Amazon’s Alexa and other conversational ecosystems, to name a few).
Virtual assistant services and other customer service management will be a major area of focus for many firms. Kore.ai has foreseen this market demand and has brought in major enhancements in its Bots Platform, such as:
- implementing open, extensible APIs for efficient integration with global enterprise systems and analytics engines
- bolstering omnichannel capabilities by growing to over 30 out-of-the-box pre-integrated channels
- enhancing the unique hybrid NLP and intelligent dialog turn management capabilities
- employing an IVR integration framework on the platform with advanced contact center AI capabilities with integration to leading IVR, speech recognition and text-to-speech platforms
- expanding global reach with support for languages including English, French, German, Spanish, Chinese, Portuguese, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, Dutch and Bahasa
- innovating the Universal Bot – one master assistant that routes requests to several backend chatbots across different functions and domains as needed
- creating an advanced AI based knowledge extraction and ingestion feature set to take structured and unstructured content to produce bot knowledge
- creating a new state-of-the-art proprietary AI framework to discover intents, sub intents, entities and discourse patterns from historical chat and call transcripts to enable rapid conversational AI bot creation and ongoing optimization
AI in 2019 will feature more unique breakthroughs, disruptions, and products. Watch out for more exciting developments in the year ahead.
[ls_content_block slug=”contributor-article-disclaimer”]