Back in 2017, the global AI in the FinTech market was worth 1,337 million.
By 2025, it is expected to grow to 7,305 million, according to Markets&Markets research.
Most probably, you’re already using AI in your everyday financial operations—like chatting with bots or giving voice commands—but don’t pay attention to it.
In this guide, I’ve collected 5 AI-powered technologies that solve financial problems in 2020, how they do it, and what companies take advantage of AI in FinTech.
Let’s check them out.
#1. Chatbots
Almost half of the organizations are already using bots or have an active project in place, according to Personetics.
What’s a chatbot? It’s a software that simulates a conversation or chat through messaging apps, websites, or phone calls.
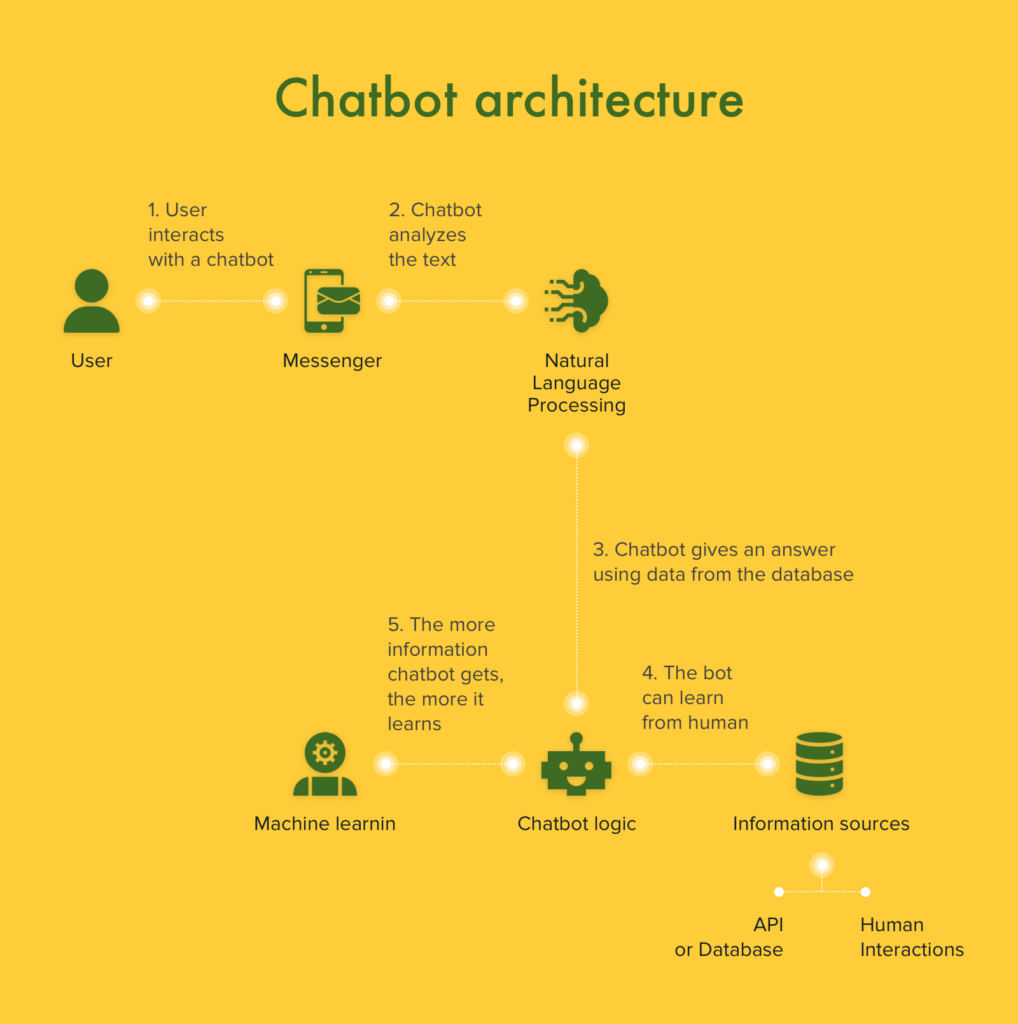
AI-powered chatbots use machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence to understand a customer’s message—as well as their intentions—and generate answers. They deeply analyze users’ messages and moods to provide better feedback.
AI chatbots learn from people: the more you train them, the better they become.
Chatbots bring enormous benefits to FinTech:
-
Let users transfer their money second-fast
-
Answer simple customers’ questions
-
Automate mundane tasks—transfer money, check account status, make payments
-
Entertain next-gen users—20-35 y.o. people who spend most of their time in smartphones
-
Save costs—you don’t need to pay an actual CS department, just the programmer who will make the bot
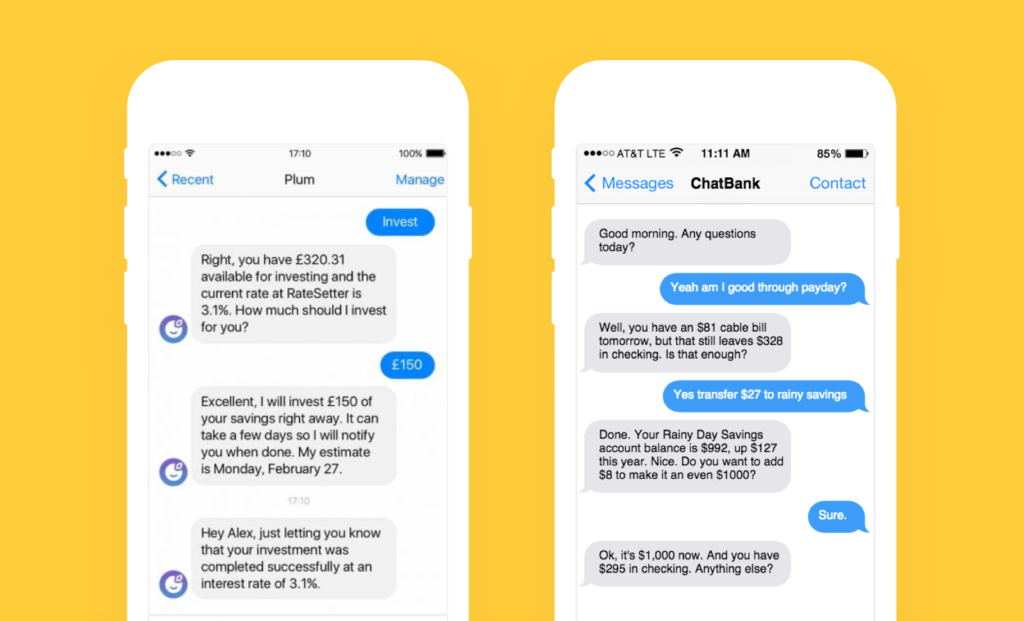
#2. Digital Financial Advisors
Although robo-advisors are similar to chatbots, they’re not regular AI-helpers. Their job is to handle more financial-specific tasks. They include:
-
assess investor’s tendency to risk
-
choose a strategy of investment
-
sell/buy securities per the selected exchange rate
-
approaching any transaction limit
-
verify notifications
-
manage dividends
They’re more like your personal banking manager who helps you navigate savings, make financial plans, and use your money wisely.
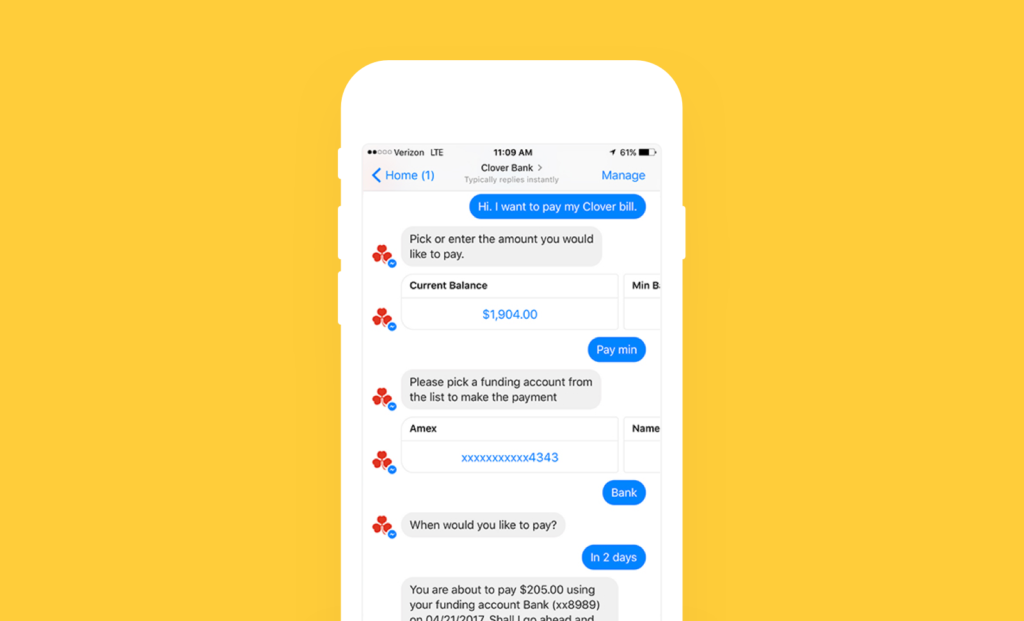
Virtual assistant Ella is an excellent example of a customer’s bill payment chatbot. It sends bill-ready and payment-related notifications and reminders using channels like Facebook Messenger, Amazon Alexa, and Google Assistant. And it can be customized to match a company’s branding.
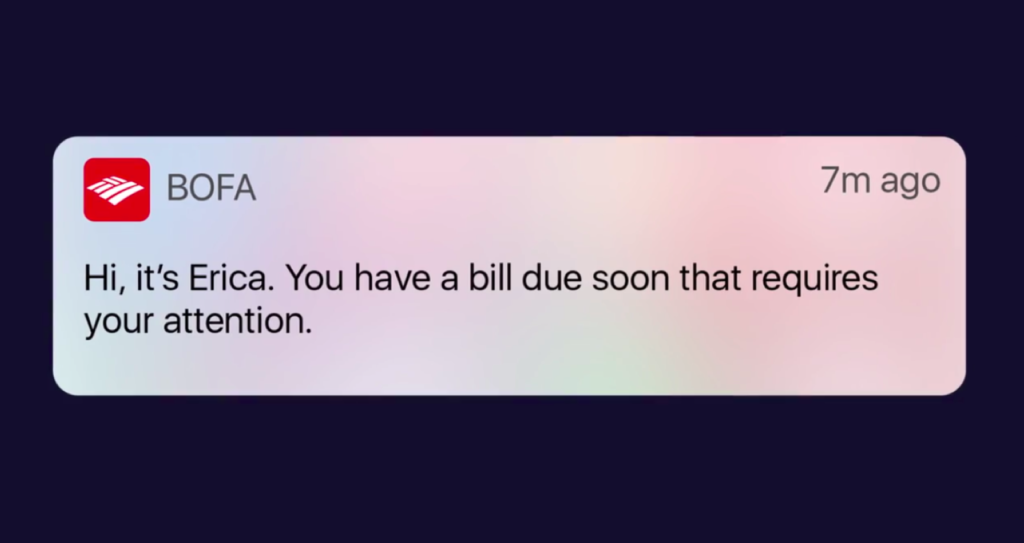
Bank of America, integrated Erica, another virtual assistant, right to their mobile banking app. Erica notifies users of important credit score changes, refunds, sends bill reminders, watches over the money balance, and shows duplicate charges.
And that’s just some of the things it can do.
#3. Voice Recognition
When people call their bank, most often, they have an urgent matter to take care of.
And the last thing they want to do is waiting for an agent/listening to hold music. Then go through an authorization process—that all only increases customer’s frustration.
But such issues can be left in the past as AI and language machine learning are transforming the voice-driven customer experience through speech recognition.
Speech recognition systems understand speaking habits, slang, dialects, accents, and even a customers’ intonation. If a person is clearly frustrated or there’s a need for a more human touch, the software will escalate the issue immediately so that a CS agent could step in and take charge.
It doesn’t mean that voice-recognition software could replace human agents. Instead, it’s more of an automated support staff that categorizes calls, answers basic questions, and directs customers to the right person who will help them further.
What’s more, voice recognition software can help banks authorize their customers faster. Banks are testing security features with the help of AI-based voice recognition. It can automatically confirm the identity of a customer when they call into customer service.
This way, staff members will have to deal only with critical and sophisticated requests, while software will take care of the regular ones—making payments, transferring money, and reporting stolen or lost ATM and credit cards.
VoiceKey.FRAUD, developed by SpeechPro company, identifies fraud voices in incoming calls to contact centers. First, it compares subscribers’ voices with voices from fraud databases. Then, it notifies agents or security services to take action in case of any fraudulent activity.
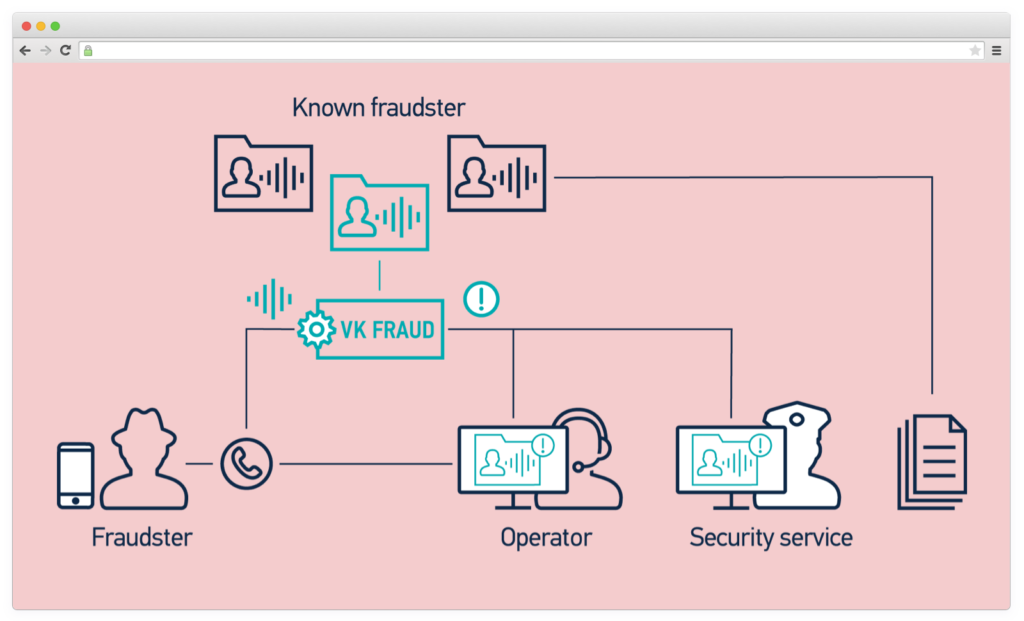
#4. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics uses several technologies like computer science, data mining, ML, and, of course, AI to prevent cyber frauds.
It combines millions of data points from transaction bank’s customers make—that’s how it discovers patterns and routine behaviors. In case of any deviations, the software sends an alert to bank officers for possible fraudulent activities.
For example, if a customer earns ~$10,000 per month, but suddenly there’s a $100,000 transaction to their bank account, the software will notify bank staff to check it out.
This way, banks improve their cybersecurity systems and strategies, especially when it comes to solutions like mobile payments, bitcoin, and blockchain.
Artificial neural networks and ML algorithms outmatch any traditional statistic method when it comes to detecting suspicious events.
For instance, ThetaRay company used unsupervised ML algorithms and big data analytics to analyze several data sources, including current customer behavior, compared to their historical behavior records.
#5. AI-Powered Models
Determining how likely a person or business is paying the loan back is critical for the whole banking sector. It may be hard to figure this out, even with all the information in-hand (but often the information is incomplete or incorrect).
That’s why some FinTech companies use AI-powered models to assess risks in seconds. Which makes it easier for bank personnel to make more relevant offers.
AI models are used for:
-
determining creditworthiness, particularly for those without credit histories
-
streamlining the loan process
-
improving customer experience for borrowers
Lenddo startup was based on checking the applicant’s digital footprint to determine their creditworthiness. It included social media accounts, internet browsing history, geolocation, and other information a smartphone can provide. Then the machine learning turned this data into a credit score used by banks or other lenders.
ZestFinance company claims to help make better lending decisions, and fast. It processes alternative data to get info on people with no or little credit history. ZestFinance uses Baidu (Chinese browser) to search for data and make credit scores for individuals. It gives them a massive amount of data for the Chinese market, where credit score systems are often lacking.
ZestFinance software will use Baidu’s search, location, and payment data for people. This way, ZestFinance can help lenders figure out the creditworthiness of Baidu users—even if these users have very little or no credit history.
AI-powered technologies move financial companies who adopt them to an entirely new level. AI processes information faster constantly learns and improves, and adopts new skills in record time. It helps to deliver better customer service, protects from cyber frauds, makes predictions, and many more.
The growth of data processing, enhanced ML algorithms, more affordable development costs, and high demand—this all leads AI to a full-fledged involvement in FinTech.
AI is not perfect (not yet, at least). But on the whole, it gives many more benefits than challenges to the FinTech industry.
Image credits
Screenshots by author.